301 redirects, XML sitemap, canonical tags, and other SEO terms may be unfamiliar to you. But in the digital marketing era, these terms will save you from making bad decisions. Read on to discover a comprehensive SEO glossary list.
Every business of any size can’t ignore digital marketing as one of the main ways to reach its target audience and generate more revenues.
With so much depending on your website and social media pages, you should have an SEO glossary handy.
You may hire a digital marketing agency or have an in-house team. Whatever the case may be, SEO terminologies will help you better understand the strategies and actions of your digital marketing team.
In this post, we cover 250+ SEO terms in an easy-to-understand language so that even beginners can get a headstart.
A
1. Above the Fold
What you see on a webpage without scrolling down – the header, title, a visual, or a video. Good SEO practice is not to fill the above the fold of your website with ad spaces. This will deter the visitor from staying on and increase the bounce rate.
2. Advanced Search Operators
Adding special symbols and characters for a more specific search query.
3. AJAX
A kind of programming, AJAX stands for Asynchronous JavaScript and XML. It enables updates on a website without the need to reload the page. The page loading gets faster and is more responsive.
4. Algorithm
A formula that specifies some actions with which certain procedures are performed exactly as described. Within the purview of SEO concepts, algorithms are applied by search engines to serve up pages that rank high based on more than 200 factors.
5. New Algorithm
A new sequence of actions that are added to the existing ones to improve the search results quality. Example: Google Penguin.
6. Algorithm Refresh
The same sequence of actions is re-run by search engines.
7. Algorithm Update
When the search engine changes some actions in the current sequence.
8. Alternative Text
Also known as alt attribute or alt tag, it gives a written description of an image on a website so that visually impaired readers and robots know what the image contains. In SEO-sphere, the alt text with the keywords improves the ranking of the page.
9. Ambiguous Intent
When the objective of a searcher is not clear. It doesn’t fall in any of the search intent categories like informational, commercial, navigational, or transactional.
For example, if you type in a broad term in the search bar like vacation, the search intent is ambiguous as the search engine doesn’t know whether you’re looking for a specific type of vacation, vacation places near you, or how much a particular vacation costs.
10. AMP
Accelerated Mobile Page or AMP is a technology used by news sites and other publishers to load their pages very fast on mobile devices.
11. Amplification
A marketing term that refers to promoting a product or brand through influencers, social media, and paid ads.
12. Analytics
The process of collecting and analyzing website data through a platform like Google Analytics to set or revise a course of action.
Analytics provides you with key metrics like organic traffic, traffic source, dwell time, bounce rate, and others to set you on the right SEO path.
13. Anchor Text
The part of the content that can be clicked to take the user to another webpage or website. The anchor text is closely related to the topic and is highlighted in blue to indicate that it has been hyperlinked.
14. API
API is short for Application Programming Interface. It’s the in-between software that allows two apps to communicate with each other.
API example: Kayak or booking.com connecting to the API of a carrier and serving you information like flight dates, price, etc.
15. Artificial Intelligence
Also referred to as AI, artificial intelligence refers to computers having the ability to think like a human brain instead of solely acting out its programmed responses.
Robots are a prime example of artificial intelligence.
16. Async
Async or asynchronous refers to the technology where a process is not dependent on the completion of another process.
17. Authority
A metric to measure the strength of a domain or a webpage. Domain Authority is a proprietary tool of Moz that applies signals to a website to check how strong or weak it is.
The number of relevant backlinks on a website or webpage determines its domain or page authority. The higher the authority, the higher the ranking of the website or page.
18. Auto-Generated Content
Content that is generated through programming as opposed to created by humans. For example, password suggestions.
B
19. B2B
Business-to-business or B2B is a business format where sales and marketing take place among business entities, not individuals.
For example, when a country buys aircraft from Boeing.
The SEO theory of B2B indicates high-involvement products that are more expensive. The sales funnel is typically longer and the decisions are taken by professionals with top authority.
20. B2C
Business-to-consumer or B2C involves businesses catering to individual needs. For example, when we buy clothes from a retailer.
In the case of B2C, transactions are not of extremely high value as medium- to low-involvement products are being dealt with. The sales funnel is also shorter and the consumer is usually the decision-maker.
21. Backlink
Also known as an inbound link, a backlink is when a website gives a link to yours. In the world of SEO, if you get backlinks from high-domain sites, your site will rank higher on search engines because of your authority.
22. Bing
Bing is the search engine of Microsoft. It’s the second most popular search engine after Google and holds a market share of about 3%.
23. Black Box
A computer program that, due to confidentiality, is not properly understood. The effects of processes can be seen but the processes are not known. An apt example is Google’s algorithms.
24. Black Hat SEO
Black hat SEO is a practice that uses spammy links, keyword stuffing, text hiding in websites, and other strategies that do not adhere to the guidelines and best practices of search engines.
This can lead to websites getting penalized and decreased ranking.
25. Blog
A written content published on your or someone else’s website. Blogs are expert opinions or experiences that individuals or groups of writers can publish.
26. Bot
A bot is short for robots. Bots on search engines are programmed to perform repetitive functions.
27. Bounce Rate
A metric that measures the percentage of visitors to a website who leave without visiting other pages. The higher the bounce rate, the worse it is for a website as it shows it couldn’t hold the interest of the visitors long enough.
28. Branded Keywords
Keywords that include the name of a brand or business. These could be either organic or paid keywords.
29. Breadcrumb
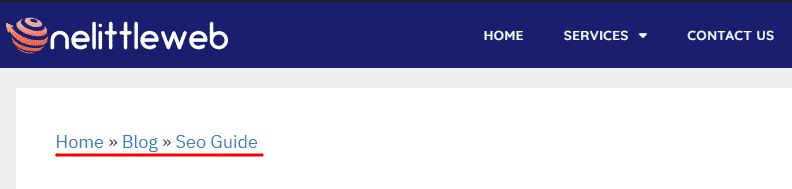
A breadcrumb or breadcrumb trail refers to the user’s location on an app or a website. It’s a navigational tool used where there is a lot of content on a website and a hierarchy is followed.
30. Broken Link
A link on a webpage that doesn’t lead anywhere as it has been moved to another location or is offline or doesn’t exist any longer. It’s a major part of the SEO glossary because page rankings suffer if they have broken links.
31. Browser
A software that gives access to the world wide web. Examples of browsers are Chrome and Firefox.
32. Bundling
Combining one or more services or resources and offering them as one. In the world of SEO, bundling copywriting and graphic designing is not recommended as these require different skill sets.
C
33. Cache
A technology that stores web page content temporarily on the browser to reduce loading time.
34. Cached Page
A page that shows the content of a website when it was last visited.
35. Canonical Tag
When there are multiple pages on a website with similar content, a canonical tag is added to a single page. It’s an HTML code that prevents the search engine from taking into account duplicate content. Therefore, only the page with the canonical tag is given authority and link juice.
36. ccTLD
This stands for country code top-level domain. For example, a company in India has .in at the end of its domain name. .in is the ccTLD.
37. Channel
The various vehicles through which content is served. Examples: social media, search engines, etc.
38. Citations
These are listings of business identities that include the name, address, and phone number on directories.
39. Click Bait
Misleading headlines with an overpromise that encourage users to click on it so that publishers earn advertising revenues.
40. Clickthrough Rate
CTR or clickthrough rate is the percentage of visits a website or webpage gets on a search engine through paid or organic SEO. It’s a measure of how attractive the title tag and meta description are to lure the visitor to click on the link.
CTR is calculated by dividing the total organic clicks by total impressions and multiplying by 100. The higher the CTR, the better it is for ranking.
41. Client-Side Rendering
A web application that uses JavaScript on the browser to serve the webpage to the user instead of from the HTML page with the help of the server.
Although the initial page load is a bit slow, the loading of subsequent pages is very fast. And because the server is not contacted every time the page is loaded, it saves time.
In an SEO context, client-side rendering needs to be properly implemented to prevent low SEO.
42. Cloaking
Showing a different version of a webpage to search engines than that to humans.
43. Content Management System
CMS or content management system is a web-based application that allows creating, upload, publish, and manage digital content. Popular examples of CMS are WordPress and Wix.
44. Co-citation
When a third party refers to two separate authorities together. For example, when speaking of search engines, we refer to Google and Bing although these seldom link to each other.
45. Comment Spam
An irrelevant comment that is left on a blog or video content and doesn’t add value to the topic. It’s a ploy to self-promote and get a backlink.
46. Commercial Intent
A search with the intent of comparing products and services to identify what fits the user the best.
47. Competition
Websites that are trying to rank on the same keywords as your website is but operate in different niches than yours. This is SEO competition.
Direct competition is business entities that sell and market the same product and service as your company. These aim at the same target market.
48. Content
Written words, images, videos, and audio files that are published on websites to impart information to a specific audience.
49. Content is King
SEO vocabulary won’t be complete without mentioning this term. It refers to the quality and relevance of published content and that it’s the single most important element that can make your SEO and digital marketing efforts a success.
50. Conversion
Conversion refers to the completion of the desired action on a webpage. For example, conversion can mean signing up for a newsletter, filling in a survey, granting an appointment, or making a purchase.
51. Conversion Rate
The number of visitors who complete the desired action expressed as a percentage of the total number of visitors to the website.
52. Conversion Rate Optimization
The steps are taken to improve the conversion rate by changing the website design, writing more attractive copy, inserting call-to-action buttons strategically, or changing the price.
53. Correlation
How two or more phenomena are related to each other. In the context of SEO concepts, a correlation between variables is tested to gauge their effect (if any) on page rankings.
54. Crawling
The act of scouring the internet by search engine bots to look for and index web pages.
55. Crawler
The search engine bots or spiders explore the web for new or updated content and index them.
56. Crawl Budget
The number of pages crawlers will explore and index from a website within a specific time frame.
If your site has many pages, Google may not be able to find and index all of them because it’s constrained by time and the millions of other websites that exist to be crawled.
Without getting crawled and indexed, a web page will not rank.
57. Crawler Directives
Instructions to crawlers regarding what to crawl and index and what not to.
Noopeners, noreferrers, and nofollows are some of these directives.
58. Crawl Error
When a webpage cannot be crawled, the search engine shows a crawl error. This could be because the page has been removed or redirected. This negatively affects the page ranking.
59. Critical Rendering Path
The process by which a browser converts JavaScript, HTML, and CSS to enable a web page to appear in a viewable format.
60. CSS
Cascading Style Sheets define how the website looks in terms of fonts and colors, irrespective of the content. It also determines how the web page appears when viewed from different types and sizes of devices.
61. Customer Journey
The process a customer takes from being aware of a product or service to purchasing it. It typically has four phases – awareness, interest, desire, and action.
The stages of the customer journey correspond to the search intent types – informational, commercial, navigational, and transactional.
To reap the benefits of SEO, a web page must be designed to make the customer journey flow seamlessly from one phase to the next.
D
62. Data
All the facts and numbers that are collected to be analyzed for strategizing.
Examples of data for SEO include customer demographics, location, search intent, and others that are analyzed for making better content for targeted communication.
63. Dead-End Page
A page on a website that doesn’t lead anywhere. It doesn’t contain any link that leads somewhere else on the website.
64. Dead Link
A hyperlink that leads to a page that doesn’t exist anymore. Dead links negatively impact SEO and page ranking.
65. Deep Link
A link that leads to some other page on the website other than the homepage. Deep links provide link juice to important content on the site.
66. De-index
When an entire website or a webpage is removed by Google from the search engine results page, it’s called a de-index. De-index is also known as delisting.
It takes place when Google’s Webmaster Guidelines have not been followed. However, you can also de-list your website or your webpage by using a Remove URLs tool found on Google Search Console.
67. Directory
A compilation of website lists where similar sites are clustered together. Businesses can either pay to be included in a directory or it could be free.
For SEO purposes, valid links from a directory add to the authority of a site and increase its ranking.
68. Disavow
To let Google know to ignore links on your site that are low-quality and spammy. The Disavow Tool from Google helps you do this to prevent your site ranking from going down.
69. Distance
Distance refers to how far the location is from the searcher to the destination point. It is relevant in the Google 3-pack search result that shows the searcher the top three destinations near them according to their search query.
70. Do-follow Link
A link that instructs search engines to follow it to its source and give it a ranking boost.
However, these do-follow links led to many spammy sources getting a high rank for no reason.
71. DOM
Document Object Model or DOM gives structure to XML and HTML documents and determines how the file can be accessed and modified by JavaScript or other programming languages.
72. Domain
The name of a website that ends in .com or .org.
73. Domain Authority
A MOZ proprietary tool that gives a website a score between 0 to 100 to indicate its ability to appear on search results.
The domain authority of a website is a measure of its strength. The higher the score, the more likely that even fresh content on the site can rank well.
74. Domain Name Registrar
The organization that keeps your domain name with it. Examples: bluehost and GoDaddy.
75. Domain Name Server
DNS or domain name server links the domain name to its IP address. It determines the right server for the user based on their domain.
76. Doorway Page
A webpage targeted to rank on certain keywords and which drives the visitor to another website. An example is multiple pages targeted at audiences from different cities that lead to the same page.
77. Duplicate Content
When there is similar content on more than one page on a website. Duplicate content brings down the ranking of a website.
For e-commerce sites, there may be very similar content on multiple pages of the same website. To address this issue, a canonical tag is used to send a signal to the search engine to take into account only the page with the canonical URL.
78. Dwell Time
The time between a click on a website link from the search results page and back to the search results.
A dwell time of fewer than five seconds on a website indicates its content may not be very useful or of good quality. Thus, it affects the expertise and authority of the website and ultimately its ranking.
E
79. E-commerce
An online platform that allows the selling and buying of goods. Example: Amazon.
80. E-commerce SEO
An SEO campaign for e-commerce that targets to rank on keywords related to SKU or product name. The campaign could also try to rank on the e-commerce brand name, a specific category, or the product page.
81. Editorial Link
An editorial or natural link is when one website links to another without asking for a return favor or without any payment.
82. Engagement Metrics
Measurements that signal how involved users are with a website or webpage. These metrics include:
- Dwell time
- Bounce rate
- Conversion rate
- CTR
- Time spent on a website or page
- Organic traffic number
- Unique visitors
- Returning visitors
- How often there are visitors
- Recency rate of visitors
83. Entity
Business organization, people, place, website, or a group.
84. External Link
An external link is also referred to as an outbound link. It’s the link that one website provides to another and that’s not within its own site. For example, Wikipedia contains lots of external links that take the visitor to other sites.
F
85. Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation or faceted search allows searchers to make their searching easier by offering filters on the page.
For example, filters according to shoe size, price, or simply a specific type of shoe make it more convenient and time-saving for the user to find what they are looking for instead of browsing through hundreds of pages.
This is especially useful on e-commerce sites or sites with a large list of products.
86. Fetch and Render Tool
A tool on Google Search Console that allows you to see your webpage in the same way Google views it.
87. Featured Snippets
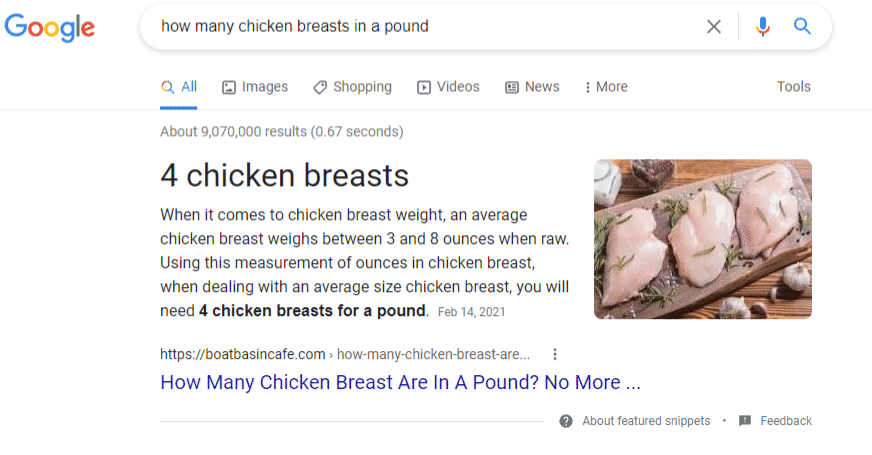
A block of answers above the organic search results. It’s also called position zero as it appears above the number one organic search result.
This block shows a snippet of long-form content and highlights brief answers to informational queries. It provides the link to the entire content.
Examples of featured snippets include a video carousel, recipe snapshots, a list, or a table.
88. File Compression
A sequence of steps whereby a file is made lighter to reduce its size. File compression of images can improve the loading speed of a website and increase its ranking.
89. Findability
How easily a website or webpage can be found by a search engine or a user.
If a webpage cannot be found, it won’t get indexed or ranked.
90. Footer Link
A footer link is a link that can be found at the bottom or footer section of a webpage.
91. Fresh Content
Updated content on a website that is refreshed monthly or weekly by adding new info to existing content, publishing a new blog, or changing a meta description or title.
92. FTP
FTP is short for File Transfer Protocol, a technology to move files from one computer, website, or network to another.
G
93. Geographic Modifiers
Businesses add geographic modifiers to show their location or the areas where their services are available. For example, “iStores in Chicago”.
94. Google
The number 1 search engine in the world was founded in 1998. It uses more than 200 factors to signal page ranking.
95. Google Ads
Google Ads is the paid advertising platform that shows businesses like yours when someone searches for it. You can pay to have your business appear on Google and Google Maps. You only need to pay when someone clicks on your ad.
96. Google Analytics
An online software from Google that collects key information from a website like the number of organic traffic, traffic source, conversion, how visitors interact with the website, etc.
These are presented on charts in Google Analytics to help businesses analyze and interpret the results to formulate business strategies.
97. Google Bombing
Also known as Googlewashing, it’s a practice whereby a target page ranks high for an irrelevant search phrase when many websites link to it with anchor text.
It’s a black hat SEO tactic that is not recommended. Real SEO serves up relevant results whereas Google bombing doesn’t.
98. Googlebot
Googlebot is the crawler or spider that explores the web to find new content or pages to index.
99. Google Hummingbird
An algorithm from Google that was released in 2013 to match the search intent of the user with more relevant results. It put more emphasis on semantic words rather than the exact keywords to come up with more relevant results.
100. Google My Business
A business listing on Google that has the name, address, and phone number of business entities. Getting your business enlisted here is a good SEO tactic to increase the website ranking.
101. Google Panda
First released in 2011, this is an algorithm from Google that made a sea-change in website authority and ranking. It targeted to downgrade websites with low-quality content and spammy links and increase the ranking of high-quality sites.
102. Google Penguin
Another algorithm from Google, the Penguin version was released in 2012 to lower the ranking of websites that used keyword stuffing and low-quality backlinks.
As a result, websites with high authority and relevant content moved up the ranking positions even though they did not overly use the keywords.
103. Google Pigeon
An update from Google, the Google Pigeon was released in 2014 to improve local searches. It gave a rank bump to local businesses that followed the best practices of organic SEO.
104. Google RankBrain Algorithm
It’s the third most important ranking signal from Google that was launched in 2015. It’s an AI-powered algorithm that looks at search keywords and how the user interacts with the search results.
Depending on the keywords, RankBrain tweaks the importance of content length, its freshness, backlinks, and other parameters to serve better results to match the search intent.
105. Google Sandbox
Google Sandbox is a tool that doesn’t allow new websites to rank high on SERP before it has gained enough domain authority. It’s usually a period of four to six months before new websites can get a high position on search results.
106. Google Search Console
Free online software from Google that allows you to track and measure the performance of your website. Search Console also identifies technical issues on your website so that you can fix them and optimize your site.
107. Google Trends
A tool from Google that shows the trending topics of the day. This term is a key part of the SEO glossary as it can hint at content creators about the trending topics to write about and rank on.
108. Google Webmaster Guidelines
A set of guidelines from Google that sets out the good and bad practices by which a website can be upgraded or downgraded (or completely de-listed) on the search engine, thus affecting its ranking.
109. Gray Hat
Gray hat SEO practices are a mix between adhering to Google Webmaster Guidelines and relaxing some of the rules a little.
110. Guest Posting
Guest posting, also known as guest blogging, is writing a blog and publishing it on someone else’s website.
This is a backlink-building strategy as it aims to gain a backlink to the blogger’s website through the guest post published on another site.
H
111. Heading
A heading is a way to mark the main title and subsequent sections within a content.
H1 to H6 headings are used to break up a large content into different sections. The descending order of the headings signals the level of importance of each section, H1 being the most important one.
Headings make it easy to read and also help the content to rank high on search results owing to its good structure and its use of the main keywords.
112. Head Term
The main keyword with a short tail that is difficult to rank on. For example, SEO.
113. Hidden Text
A black hat SEO practice that hides some texts in web content by using the same color as the background or using very small fonts or using a technology that doesn’t show the text on the screen.
These texts are laden with keywords and artificially boost the page ranking.
114. Hilltop Algorithm
The Hilltop algorithm was acquired by Google in 2003. It’s used to zero in on web content written by experts.
These expert documents have topics written on a specific topic and link out to multiple sites.
115. HITS Algorithm
HITS or Hyperlink Induced Topics Search algorithm analyzes links that go both ways – from the webpage to other sites and from other sites to the webpage.
116. Holistic SEO
A complete and long-term approach to SEO to reap benefits in the future.
117. Homepage
The main page on a website that contains links to other pages on the site.
118. Hreflang
A language tag that helps Google decide which language to serve a website in when people use that language for search purposes.
119. HTML
Short form of Hypertext Markup Language, HTML is a programming language used to create a website.
120. HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol or HTTP is how information gets transferred from a server to a browser.
121. HTTPS
HTTP with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to encrypt data that is transferred to and from a server to a browser. The SSL protects data from being abused.
122. Hub Page
A central resource of authoritative content focused on a topic. It links out to many websites and also contains links from other sites.
I
123. Image Compression
The process of making an image file size smaller without compromising on the resolution.
124. Image Sitemap
A sitemap that contains only the image URLs of a website.
125. Inbound Link
A link from another website to your website. Also known as a backlink.
126. Index
A collection by search engine bots of all the data on the Internet.
127. Indexability
The ability of a web page to be easily found by crawlers and added to the index.
128. Index Coverage Report
A report found on Google Search Console that shows whether all your website pages have been indexed or not.
129. Indexed Page
A web page that has been crawled by search engine bots, added to the index and is ready to appear on search results when there’s a related search query.
130. Information Architecture
The structure of a website that defines how it’s organized and where its content can be found.
A flat architecture is SEO-friendly as it’s easy to navigate and find all the information.
131. Informational Queries
The type of search queries a user asks on a search engine that looks for answers to questions.
132. Information Retrieval
The steps involved in looking for information like text, videos, and images from an index and presenting it to the user as per the search intent.
133. Intent
The reason behind which a user looks up a word or term on the search engine.
134. Internal Link
A link in the content of your website that takes you to other pages on the site.
135. IP Address
Internet Protocol Address is a unique address through which devices like computers, smartphones, and tablets are identified.
Your IP address is used by the network server for communication.
J
136. JavaScript
A programming language that allows dynamic elements like links, images, videos, and others on a static web page.
However, JavaScript can lower the ranking of a site or page as it delays the loading of a page and reduces the indexability of a web page.
137. JSON-LD
JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data or JSON-LD is one of the many formats that structure a website data.
K
138. Keyword
A single word or a few words or a phrase that a user types into the search engine bar when looking for answers.
Keywords are the foundation of SEO practice as topics are written around keywords or videos made around them to increase the chances of them appearing high on the SERP position.
139. Keyword Cannibalization
When a website has more than one page that aims to rank on the same keyword. This is not a recommended practice in the SEO world as it decreases the domain authority, click-through rates, and conversions.
140. Keyword Density
The number of times a keyword is used in a content. To calculate the keyword density, divide the number of times the keyword appears in the content by the total word count and multiply by 100.
A keyword density of 1-2% is mostly recommended by experts.
141. Keyword Difficulty
An estimated score by Moz that indicates the level of difficulty to rank on specific keywords as competitors are already ranking high on them.
142. Keyword Research
The process of finding out how many times per month a keyword is searched for by users. This can be filtered by country or globally.
Keyword research reveals how competitive a keyword is and how well competitors are ranking on it.
143. Keyword Stuffing
Using the keywords too many times in a single content in an attempt to rank high on search engines. This is a black hat SEO practice that ends up with the website getting penalized.
144. Knowledge Graph
A graphical representation of interlinked events, concepts, or objects. Using semantic metadata and linking, a knowledge graph visually presents contextual data that’s used for integration and analytics.
145. Knowledge Panel
The knowledge panel from Google appears on the top or the right side of the search results page. It shows details related to the search query
146. KPI
KPI or key performance indicator measures results against business and marketing objectives and goals.
L
147. Landing Page
A landing page is a standalone page on a website where a visitor lands by clicking on a link provided in a newsletter, an ad, an email, or from any other online location.
The purpose of a landing page is to get the visitor to perform some action that leads to conversion.
148. Lazy Loading
A technology that delays the loading of a page until the time it is needed. Lazy loading improves the overall page speed.
149. LSI Keywords
LSI or Latent Semantic Indexing keywords are words and phrases that are closely related to the seed keyword. For example, LSI keywords for Keto would be low-carb diet, high-protein diet, Keto recipes, etc.
150. Lead
A lead is a potential customer who has shown some kind of interest in your product or service by filling up a form or downloading a free resource or guide.
151. Link Building
The process of getting inbound links or backlinks from websites of high authority to your website to make it rank higher on search engines.
Link building involves outreach emails to bloggers and influencers, getting listed on business directories, publishing high-quality content that gets natural links, paying to have your links in sponsored content, or getting into partnerships.
152. Link Equity
The value of a link as indicated by its expertise, authority, and trustworthiness.
153. Link Exchange
A practice where websites agree to exchange links to artificially bump up their search ranking. This practice violates Google Webmaster Guidelines if done in excess.
154. Link Farm
Another black hat SEO practice, a link farm is an artificial way to lend links to each other among a group of websites to increase the ranking of each.
155. Link Juice
Authority sent through links to strengthen the pages that receive the links to increase the ranking.
156. Link Profile
The credentials of a link that points to the quality of the linking website. The quality is determined by how the links were collected and the anchor text used.
157. Linked Unstructured Citations
When a non-directory platform like news or blog mentions partial or full contact information of a business.
158. Link Velocity
The speed with which a website acquires links. A spike in link velocity could indicate spammy links or because of marketing viral content, or doing something that catches the attention of the industry.
159. Local Busines Schema
Structured data about a business with their name, address, and phone number that help Google understand basic business information.
160. Local Pack
Also called the 3-pack, the local pack is the group of three local business listings on Google Maps that appear when a user searches.
161. Local Queries
Search queries where the user is looking for something within their location of work or home.
162. Local Search Marketing
The process of online promotion of a business that has a local presence so that it shows up on Google Search.
163. Log File
A record that notes down the online activities of users including their personal details, IP address, and others.
164. Log File Analysis
Analyzing and interpreting the log file records to spot trends, how users interact on the sites, and their psychographic and demographic characteristics.
165. Log-in Forms
Content that needs the user to log into before getting access.
166. Long-Tail Keywords
Keywords that have multiple words instead of just one to three words. Long-tail keywords are more specific, for example, “exercises for women above 50 years old”.
It’s easier to rank high on long-tail keywords as short-tail ones are more competitive and leading businesses already rank high on them.
M
167. Machine Learning
Part of artificial intelligence that uses data to make sense of complicated processes without human help.
168. Manual Action
Manual action is a Google penalty handed to a website or certain web pages when a human reviewer identifies that it hasn’t adhered to the Google Webmaster Guidelines.
169. Meta Description
A descriptive tag that is added to the header section of every web page to show the search engine crawlers what the content is about.
A snippet of the meta description can be seen on the search results right below the title.
When a meta description is appealing enough, it encourages high CTR that increases the page ranking.
170. Meta Directive
Codes that are found on the header part of every web page that instruct crawlers on how to index each page.
171. Metric
A measurement to gauge the success or failure of marketing and SEO efforts.
172. Minification
To remove unnecessary characters from the source code without affecting the functionality.
173. Mobile-First Indexing
Google’s way of discovering and indexing websites based on the mobile device version, not the desktop version.
N
174. Natural Link
Same as an editorial link that is placed naturally in content without asking for a link in exchange.
175. Navigation
The links on a website that direct the visitor to other pages on the site. These are presented as a list on the top, side, or the bottom of the homepage.
176. Navigational Queries
Queries where the searcher is looking for a location or a page on the search engine.
177. Negative SEO
A malicious attack on competitor websites to bring down their ranking on search engines.
178. Niche
A small and specific area of interest or target market.
179. Noarchive Tag
A meta tag to signal to search engines not to keep a cached copy of a web page.
180. Nofollow
A meta tag to tell search engines not to follow an outbound link if it doesn’t want to pass link juice.
181. Noindex
A meta tag that tells the search engine not to index a webpage.
182. Nosnippet
A meta tag asking the search engine not to show the meta description snippet below your content title on search engine results pages.
183. Not Provided Keywords
Not provided keywords on Google Analytics means that Google doesn’t want to share the keywords the users used to look for a website.
O
184. Off-Page SEO
An SEO tactic that takes place outside the website. It involves getting backlinks, social media interactions, content/email/influencer marketing to create brand awareness and generate interest.
185. On-Page SEO
Optimizing for SEO within the website by posting quality content, structuring the content using H1, H2, etc. sub-headings, adding images, speeding up page load time, and others.
On-page SEO is within the control of the website owner as everything takes place on the site.
186. Organic Search Results
The results of a query that appear on a search engine page without having had to pay for them.
187. Orphan Page
A page on a website that is not linked to by any other page.
188. Outbound Link
Also known as an external link, an outbound link is a link from one website to another.
P
189. Pagination
The process of splitting one long content into pages. The pagination tag helps Google to serve the pages sequentially to the user.
190. PageRank
Google’s way of assigning an authority score to a web page based on the quality and quantity of backlinks it has. A higher PageRank means a higher domain authority.
191. Page Speed
The time it takes for a page to load on the browser. A low page speed negatively affects page ranking.
192. Pageview
When there’s a view of a full page on the browser.
193. Paid Search
As opposed to organic search, paid search is when websites pay for each click to Google to have their page appear on top of the search engine results page.
194. Pay Per Click
Pay per click or PPC is a form of advertising on Google where the marketer pays Google only when a visitor clicks on the link. The pay-per-click price is dependent on the highest bids, competition, relevance, and the history of the marketer’s account.
195. PBN
PBN or private blog networks is a group of websites that pass links to each other to artificially inflate their rankings on search results. It’s the same as a link farm and is discouraged by Google.
196. People Also Ask
A section that appears on search engines that shows questions and answers closely related to the search query of the user.
197. Persona
A persona or buyer persona is an approximate representation of the target person for marketing products and services. It’s based on collected data and includes the demographics, geographics, psychographics, and attitude and behavior of the person.
198. Personalization
Results served on the search engine based on the search history and geographic location of the user.
199. Pogo-Sticking
The act of a user going back and forth from one search result link to another on the SERP.
200. Programming Language
Writing codes and instructions in a language that can be understood by the computer. Example: JavaScript.
Q
201. QDF
QDF stands for query deserves freshness. It means that the search engine might serve results that have fresh content from new web pages.
202. Quality Content
Content that is relevant to the keyword, offers value to the readers, and is structured perfectly to make it an easy read.
203. Quality Link
A link that originates from a website that is high on expertise, authority, and dependability.
204. Qualified Lead
A website visitor who is identified as a potential customer by the action they take on the website like making a call, asking for an appointment, and similar actions.
205. Qualified Traffic
When visitors who visit a webpage are relevant to the page topic, making it likely that they will take positive action on the page like signing up or downloading free content.
206. Query
The word or group of words a user enters into the search bar of a search engine.
R
207. Rank
The position of the webpage that appears on the search engine results page.
208. RankBrain
A Google algorithm that uses machine learning to sort out the most relevant search results to queries.
209. Ranking Factor
Ranking factor or ranking signal is any of the more than 200 attributes that Google assigns to a website for it to show on its search results.
The ranking factors work together to determine where in the search results should webpages be shown according to how well (or not) they address search queries.
210. Reciprocal Links
Links that are exchanged between websites.
211. Redirect
A redirect is a page that a user or search engine is directed to from the link they clicked on. Instead of landing on the page they clicked on, they are taken to another one.
When a website is being relocated, it can show a temporary redirect like a 302 error. You will see a 301 error if the website has shut down permanently.
212. Referrer URL
The URL that sends a visitor to your website through a link.
213. Referral Traffic
Traffic that doesn’t come directly to your website but is routed through some other platform. For example, a link on Facebook that lands visitors on your website is referral traffic.
214. Regional Queries
Search queries particular to a specific location.
215. Reinclusion
After getting de-indexed, a re-inclusion is a request for the webpage or website to be indexed by the search engine.
216. Relevance
The relation of the content to the search query of the user. The more relevant the content, the higher chances it has for showing on search results.
217. Rendering
The process of converting the codes on a webpage to a viewable page by a browser.
218. Reputation Management
The steps that are taken to protect the positive image of a brand or influencer online while showing fewer or no negative comments.
219. Resource Pages
Webpages that contain a list of website links that are helpful to the user. It’s a way to gain backlinks.
220. Responsiveness
It refers to how well a website has been designed to appear equally well on mobile devices and computers without losing image resolution or cutting out texts.
221. Rich Snippets
Rich snippets or rich results are the results on search engine pages that show more than just text. Images, reviews, recipes, or lists.
To enable rich snippets, structured markup is added to the HTML files to help search engines better understand the content and serve more relevant results.
222. Robots.txt
A text file on a website that instructs crawlers where not to go. Such pages include log-in pages, cart pages, etc.
223. ROI
ROI or return on investment is the measure of success or failure against the investment in SEO. For example, your website ROI shows you how much organic traffic you have gained after you invested in backlink-building.
S
224. Schema
Codes on a webpage that structures the information in a way that crawlers can extract them and show them as a rich snippet on the search results page.
225. Scrape
The process by which search engines use a computer program to copy information from a website for indexing.
226. Scraped Content
Copying content from other websites and publishing it on your site without permission.
227. Scroll Depth
A technique that shows how far a visitor scrolls down a webpage.
228. Search Engine
A key part of SEO glossary, a search engine is a program that receives queries and serves multiple results that are relevant to the search query. Search engine examples are Google, Bing, Yahoo.
229. Search Engine Marketing
A combination of paid and organic activities targeted to increase the ranking of a website or webpage.
230. SEO
SEO or search engine optimization is the act of making the content of a website such that it appears organically on search results pages. SEO includes on-page (technical) and off-page (marketing) strategies.
231. SERP
Short for search engine results pages, SERP is the page you see after you have typed in a query in the search bar of the search engine.
232. Search History
A history of all the websites you visited that’s stored on the browser.
233. Server-Side Rendering
Rendering a website through a server instead of from a JavaScript-enabled browser. This lengthens the process between the page request and the rendering. However, server-side rendering makes it easier to crawl and index for SEO purposes.
234. Search Volume
The number of times a keyword is searched for per month. A higher search volume indicates a lot of people are looking up this term and it could be a good topic to create content on.
235. Seasonal Trends
Search queries that go up and down by season. For example, Christmas gift is a seasonal trend.
236. Seed Keywords
The main keywords used to refer to a product or service. For example, the seed keywords for a coffee brand would be “coffee”.
237. Share of Voice
Share of voice measures the number of impressions a website gets in response to a search query when compared to the total impressions received by competitor websites for the same keywords.
238. Short-Tail Keywords
Keywords that are one to three words long. These are broad terms and very competitive. Short-tail keywords cannot be ranked high through SEO activities.
239. Sitelinks
Sitelinks are the links to various pages on your website that appear below the main website link of search results.
Sitelinks show relevant page links at a glance for better user navigation.
240. Sitemap
A list of pages on a website that is structured for easy indexing for search crawlers and users.
A sitemap with an HTML format organizes the website by topics so that they can be found easily by users.
On the other hand, a sitemap that uses XML format is meant for crawlers to find a list of web pages easily.
241. Sitewide Links
Links that are found on all the pages of a website, either on the side or at the footer.
242. Site Speed
The time it takes for a group of web pages on a website to load.
243. Site Structure
The way the content of a website is organized. For example, the homepage is the introductory or main page and the most important one. Other pages come secondary to the homepage.
244. Social Media
Apps and sites like Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, etc. where users can interact with others, create, upload, share, and consume content like videos, static images, and texts.
245. Social Signal
An attribute that points to the authority and the degree of influence that social media accounts have. These don’t directly influence the ranking on Google.
246. Spam Score
A Moz tool that assigns a score to a website to show how likely it is to get penalized for spam content.
247. Spammy Techniques
The use of techniques to get a ranking that does not abide by the webmaster guidelines. Black hat SEO uses spammy techniques like keyword stuffing.
248. Spider
Crawler or search engine bot.
249. Split Testing
Also known as A/B testing, split testing tests two versions of an ad or a webpage to gauge which one gets a better response.
250. Structured Data
Structured data or schema markup organizes information on a website so that crawlers understand the content.
251. SSL Certificate
Secure Sockets Layer Certificate ensures the privacy of the data that’s exchanged between a browser and a server. Websites with the SSL certificate appear as HTTPS rather than HTTP.
252. Status Codes
Codes that show in response by the server when a link is clicked or a form is submitted or a web file is requested.
Examples: 404 (Not found), 503 (Service unavailable), 200 (OK), 410 (Gone), 500 (Internal Service Error).
253. Subdomain
A domain of a lower hierarchy that resides within the main domain. For example, https://hangouts.google.com/ is a subdomain of Google.com
T
254. Taxonomy
The process of structuring information on a website by categories to facilitate its getting found by users and help them perform tasks on the site.
255. Thin Content
Content on a website that offers no value to the users.
256. Thumbnails
A smaller version of a larger image.
257. Time on Page
An approximate measure of time a user spent on a webpage.
258. Title Tag
A meta tag added to the HTML file of a webpage to show its title. The search engines show the title tag on the search results. Therefore, using the keywords in the title tag increases the chances of a higher CTR.
259. Top-Level Domain
The main domain extension like .com, .org, .info, and .net
260. Traffic
The crawlers and people who visit a website.
261. Transactional Queries
Search queries that give a signal to the search engines that the user is ready to make a transaction. For example, searching for Providence to New York airfares qualifies as a transactional query.
262. Trustworthiness
The level of dependability on a website based on its correct information, useful and relevant content from experts, and its strict adherence to webmaster guidelines.
263. TrustRank
A Google algorithm that conducts a link analysis to separate webpages with quality content from ones that use spam. TrustRank helps genuine web pages rank high.
U
264. UGC
Short for user-generated content, it refers to a piece of content like a video, comments, images, etc. that has been created by a user.
265. Universal Search
Universal search or blended search is the search result extracted from various specialty resources and shown on the same search result page. Universal search results may show images and videos besides text.
266. Unnatural Link
A spammy link that qualifies for a penalty.
267. URL
URL or uniform resource locator consists of a string of characters particular to a website or webpage. Example: www.google.com
268. URL Folders
Parts of a website that are housed within the main web domain but separated by a slash. For example, https://onelittleweb.com/blog/ where /blog is a URL folder.
269. URL Parameters
Also known as query strings, URL parameters are elements added after a question mark on the URL to track information or organize content.
270. Usability
Usability refers to how easy it is to use a website. It depends on the site structure, design, page speed, and other factors.
271. UTM Code
Urchin Tracking Module codes can be added to a URL to get more information like the source of a click or the medium through which the click came or the name of the campaign.
272. UX
UX or user experience is the positive, negative, or mixed feelings a user gets when interacting with an app or a website.
V
273. Vertical Search
Search on a platform that retrieves only one type of results. For example, only videos on YouTube or only reviews on Yelp.
274. Virtual Assistant
A bot that listens to the user command and does actions based on them. For example, Google Assistant giving directions on Google Maps.
275. Visibility
The position that is occupied by a website on the SERP that encourages high viewing.
276. Voice Search
Searching by speaking into a smartphone instead of typing into the search bar of a search engine.
W
277. Webmaster Guidelines
Rules set by search engines that websites should go by to avoid getting penalized.
278. Webpage
A page from a website that’s visible on a browser.
279. Website
A group of web pages that form an entire site and are hosted on the World Wide Web.
280. Website Navigation
Organizing the web pages in a way that makes it easy for the user to go from one page to another or from one section to another section on the same page.
281. White Hat SEO
Clean SEO practices that abide by the webmaster guidelines.
282. Word Count
The total number of words in a piece of content.
283. WordPress
One of the leading content management systems.
X
284. XML
Short for extendible markup language, XML is a format used by websites to organize data in a way that search engines understand.
285. XML Sitemap
A list of all the web pages in a website for the search engines to crawl and index.
286. X-robots-tag
A tag attached to a web page to indicate how crawlers should crawl or index it.

Sujan Sarkar is one of the co-founders of OneLittleWeb. He leads the agency with over a decade of experience.
In 2018, he founded OneLittleWeb, driven by a vision to fill a void in the industry, providing top-quality SEO and backlink services.
His impressive track record includes crafting over 25,000 backlinks for more than 1100 clients, generating over 1 billion in traffic. This has earned him a significant presence in the SEO realm.
He successfully leads a dedicated team of 65+ SEO professionals, focused on helping SaaS and Enterprises scale their organic traffic.
Sujan firmly believes that the best backlinks are not paid for but earned through high-quality content and strategic relationships.
Every day, he works tirelessly to position your business at the forefront of your customers’ minds, striving to elevate your brand’s visibility and authority.
His daily inspiration centers around securing client features on top-tier publications like Forbes, MSN, BBC, Yahoo, and many more. He leverages the right SEO strategies to achieve this mission.