As a content marketer, much of your success revolves around the SEO strategy you follow for your website. If you do them right, you will have a better ranking, increasing traffic, leads, and conversions.
However, while doing SEO for your webpages, some issues may appear that will not only hurt your ranking but also ruin your business completely. One such problem is having duplicate content.
Going on top of the SERP depends a lot on how you handle this issue. While ignoring it can ruin all your SEO efforts, fixing it can improve your ranking and save you from Google’s penalty.
Duplicate Content & The Reasons Behind It
Duplicate content refers to multiple blocks of content found either on the same or different websites that are identical to each other. These articles can be completely matched or appreciably similar.
Which content is called duplicate:
- Your blog post copied onto another website.
- Your home page with multiple URLs that serve the same content: for example, http://abc.com, http://www.abc.com, and http://www.abc.com/index.htm.
- Duplicate pages due to URL parameters and session IDs. For example, http://abc.com/product and http://abc.com/product?sessionid=5976281.
- Pages with affiliate codes, such as http://abc.com/product and http://abc.com/product?ref=name.
- Printer-friendly pages with content similar to your web content.
There are a number of factors that can cause a duplicate content issue. From the above examples, you may already understand that most of them are technical issues.
Here are some of the causes that generate duplicate content.
Session IDs
Session Ids are used to keep track of your users as they visit your website and purchase items. One of the most common ways to maintain that session is to use cookies.
It’s quite unusual for search engines to store cookies. It makes some systems retreat from using Session IDs in the URL. because of this, each of the internal links on that website gets that Session ID added to the URL.
Since every one of those Session IDs is unique to that particular session, it generates a new URL that contains similar content.
Not Understanding The Concept of a URL
It happens when a developer starts to see the URL in a way different than the search engine does.
Developers speak a different language than the search engines. They consider the ID in the database as a unique identifier of the content, where a search engine identifies the content using URL.

Since the website’s software lets the same content in the database retrieve through different URLs, it creates duplicate content.
Content Syndication
If your website is a popular one, chances that other websites will use your article, with or without your permission.
If they don’t give you any credit or link to your original content, Google can’t identify which website is the genuine owner of that content. It has to deal with either of those similar articles, which ultimately leads to a bigger problem.
URL Parameters for Tracking Purposes
Another key reason for having duplicate content is adding a parameter at the end of a URL that doesn’t change the content of that page but acts as a different web page.
For example, http://www.abc.com/keyword-x/ and http://www.abc.com/keyword-x/?source=rss are different URLs to the eyes of a search engine, but they contain the same content.
Using such parameters may help you track or sort a product, but they surely generate a duplication issue.
Comment Pagination
Whether you’re using WordPress or other CMS, you will find an option called comment pagination. Opting for that option will lead your content to be duplicated across the URL.
The URL then will be duplicated as URL+comment-page-1, comment-page-2, and so on.
The Order of Parameters in URL
This is what happens when the CMS doesn’t use a simple and clear URL. If you look carefully, you will see some websites use parameters in the URL, like www.abc.com/?id=1&cat=2. Here, id refers to the content and cat means category.
Now, in most website systems, changing the id and cat may lead to the same result. For example, www.abc.com/?id2&cat=1 may lead to a similar page, but for a search engine like Google, they are entirely different URLs.
Printer-Friendly Page
Sometimes, your CMS produces printer-friendly pages that you link inside your content. In that case, search engines will find them and show them in the search results, which leads to duplicate content issues.
How to Get Rid of Duplicate Content
Having duplicate content is extremely harmful to your SEO effort, as well as your website. The link juice will be distributed among the URLs having similar content, meaning that your chances of ranking higher will be reduced.
Besides, Google hates duplicate content. It will penalize you and remove your site from the search results, causing you a severe loss.
However, the good news is, you can fix this issue. If the duplicate content is generated by other sites that copied your content, you can send them a polite email, asking them to remove it or give you the credit.
But, if the issue generates in your own site, you can deal with it using the following ways.
Using Rel=“canonical”
Using this HTML tag is one of the most effective ways to transfer the SEO juice from a duplicate page to yours.
You need to add the Rel=“canonical” tag to a certain page, which tells Google this is the page you want it to index.
After identifying any page with the duplicate article, Google transfers all the SEO juice from those pages to your canonical page.
This method doesn’t require removing old pages. Google will simply consider them as a duplicate version of your existing pages. Since they are not getting any link juice, you will not be penalized.
Hreflang Tag
Using the Hreflang Tag lets you tell Google that a page is related to other pages in different provinces and languages.
For example, your website is https://abc.com, and you’ve got a Spanish version of that site. Using this HTML tag will help make Google serve that page to Spanish website searchers.
So, how can this be done?
You need to implement the Hreflang annotation in the HTML page of your website. However, if you don’t have an HTML page, you can place this tag in the HTTP header.
Once done, the tag will look like this.
HTML: <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”en”href=”<https://www.abc.com>”>
HTTP: link: <<https://www.abc.com/>>; rel=”alternate”; hreflang=”en”
Don’t forget to put links to each and every version of your page. If you don’t want to add a markup to your pages, you can also include the other language version in your sitemap.
Be careful while using this tag. If you have two versions of your page that are too similar, chances are a wrong version will be ranking for the search term.
301 Redirects
Do you want to kill the duplicate version of your page and still get the link juice from it? It’s possible with the help of 301 redirects.
This option lets you tell Google or other search engines whenever someone attempts to visit the duplicate page, you want them to send those people to your primary page.
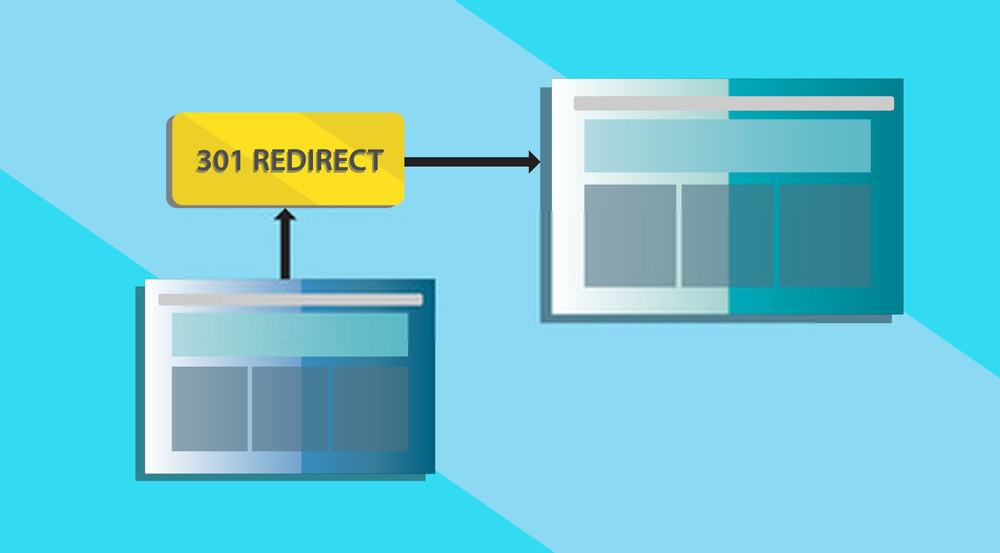
Those duplicate pages will still be there. But, unlike rel=“canonical” tags, where the duplicate page is still visible to the audiences, 301 redirects will make sure they never see anything else rather than your primary page.
Since this redirect option is permanent, you need to be careful while choosing your preferred URL.
Meta Robots Tag
If you don’t want the search engines index the duplicate pages, you can do it by simply adding the following code to the duplicate pages:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
You can also use some special characters in the “robot.txt” file to disallow the links.
However, there’s a risk.
If you block the URL, Google might find it outside of the website via links and consider it as a unique one. If that happens, your preferred page may not get the desired link juice.
Setting Passive Parameters in Google Search Console
This short-term strategy can be quite helpful if you want to quickly remove those duplicate pages that are making the SERP messy.
You can set some URL parameters in the Google search console, which will drop the duplicate pages from Google-bot indexing.
However, you’re highly recommended not to use this method. It’s because if you don’t configure them properly, Google may de-index an important page. Do not opt for this option unless it’s necessary.
Hashtag Tracking Method
Using tracking parameters in the URL may create duplicate pages with the same content. To avoid this problem, you can use a hashtag tracking method where the question mark (?) in the URL will be replaced by a hashtag (#).
What’s the benefit?
Google bots always ignore anything placed after the hashtag. So, if you have duplicate URLs like http://abc.com/product/ and http://abc.com/product/#utm_source=xyz, Google will see both as http://abc.com/product/ and won’t consider any of them as duplicate.
Declare Geo-Specific Content
If you have multiple domains for different locations, it might be difficult for you to create unique content for each of them. Then how are you going to deal with the content duplication within your location-specific domains?
You may alo like: Types of Blogs That Make Money
The process is quite simple. Go to the configuration setting option to Google Search Console in each of your domains and select the region or country of the target audience for each website.
It will avoid the confusion of the search engines, telling them which content is for which region.
How to Check Duplicate Content
Do you want to find out if your web pages have duplicate content or not? You can do it by simply copying and pasting a snippet of your article into Google search and see if there are other pages appearing with the same thing.
Apart from that, you can also use the following methods to detect duplicate content.
Using Google Search Console
Duplicate content may exist in the search snippets like meta descriptions and meta titles. You can easily detect them using Optimization > HTML Improvements of Google search console.
Using Site: Search Operator
Go to Google search page and type site: search operator/your website, along with the part of the article you want to check for duplication.
If Google shows you a message about omitted results, you know this content has a duplicate version of it.
Plagiarism Tools
Another easy yet effective way to detect duplicate content. You can use any plagiarism checker tool such as Copyscape, Grammarly premium, Quetext to check for duplicate content on your site.

Some of these tools are free and available for both Windows and Mac.
Final Thoughts
It’s difficult to find a single website that hasn’t got at least one duplicate content issue. However, the good news is, this problem can be fixed.
Now you understand the concept of duplicate content and why it happens, it’s crucial to fix them as soon as you detect them.
While duplicate content can hurt your SEO, choosing the wrong way to remove them can make the situation even worse. That’s why it’s important that you remove them using the correct way and save yourself from Google’s penalty.

Sujan Sarkar is one of the co-founders of OneLittleWeb. He leads the agency with over a decade of experience.
In 2018, he founded OneLittleWeb, driven by a vision to fill a void in the industry, providing top-quality SEO and backlink services.
His impressive track record includes crafting over 25,000 backlinks for more than 1100 clients, generating over 1 billion in traffic. This has earned him a significant presence in the SEO realm.
He successfully leads a dedicated team of 65+ SEO professionals, focused on helping SaaS and Enterprises scale their organic traffic.
Sujan firmly believes that the best backlinks are not paid for but earned through high-quality content and strategic relationships.
Every day, he works tirelessly to position your business at the forefront of your customers’ minds, striving to elevate your brand’s visibility and authority.
His daily inspiration centers around securing client features on top-tier publications like Forbes, MSN, BBC, Yahoo, and many more. He leverages the right SEO strategies to achieve this mission.